Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin, a hormone essential for converting glucose into energy. This autoimmune disorder typically manifests in childhood or adolescence, although it can occur at any age. The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Unlike Type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with lifestyle factors and can sometimes be managed through diet and exercise, Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong management through insulin therapy. Individuals with this condition must be vigilant about their blood sugar levels, as both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can lead to serious health complications. The onset of Type 1 diabetes can be sudden and dramatic, often presenting with symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
These symptoms arise due to the body’s inability to utilize glucose effectively, causing it to break down fat for energy instead. This process can lead to a dangerous condition known as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the nature of Type 1 diabetes is crucial for those diagnosed with the condition and their families, as it lays the foundation for effective management strategies.
Education about the disease helps individuals recognize symptoms early, understand the importance of insulin therapy, and appreciate the need for regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
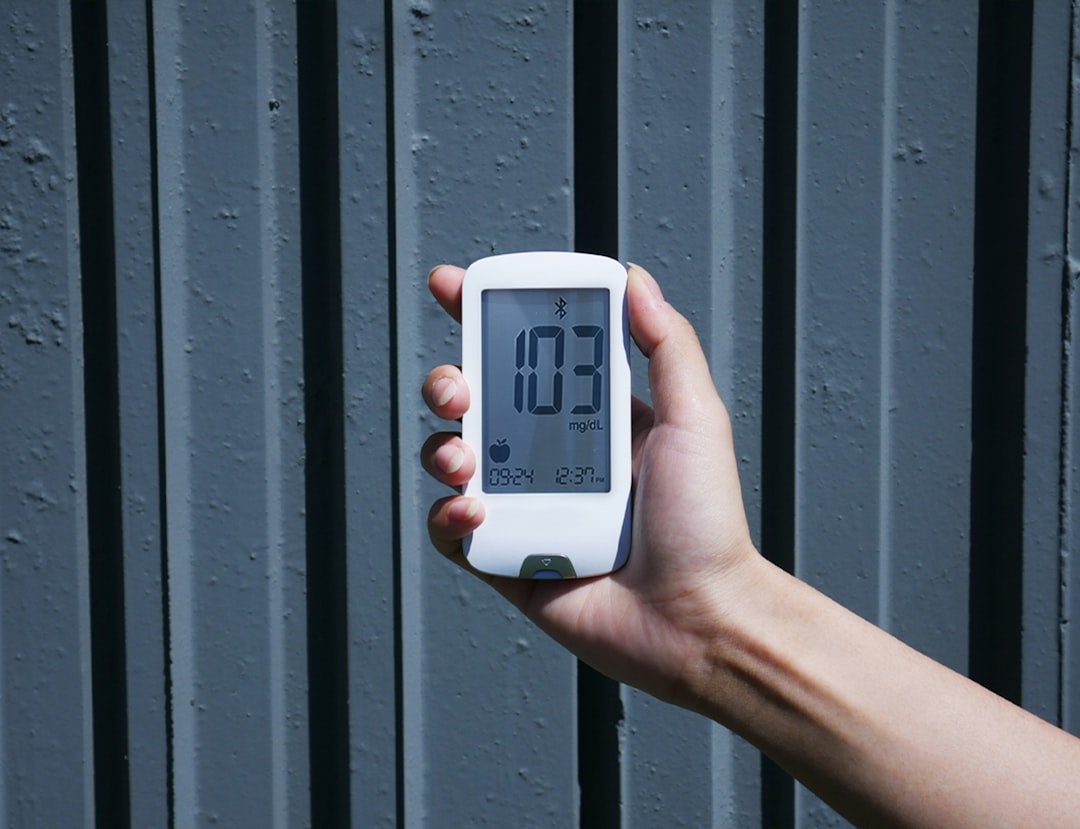
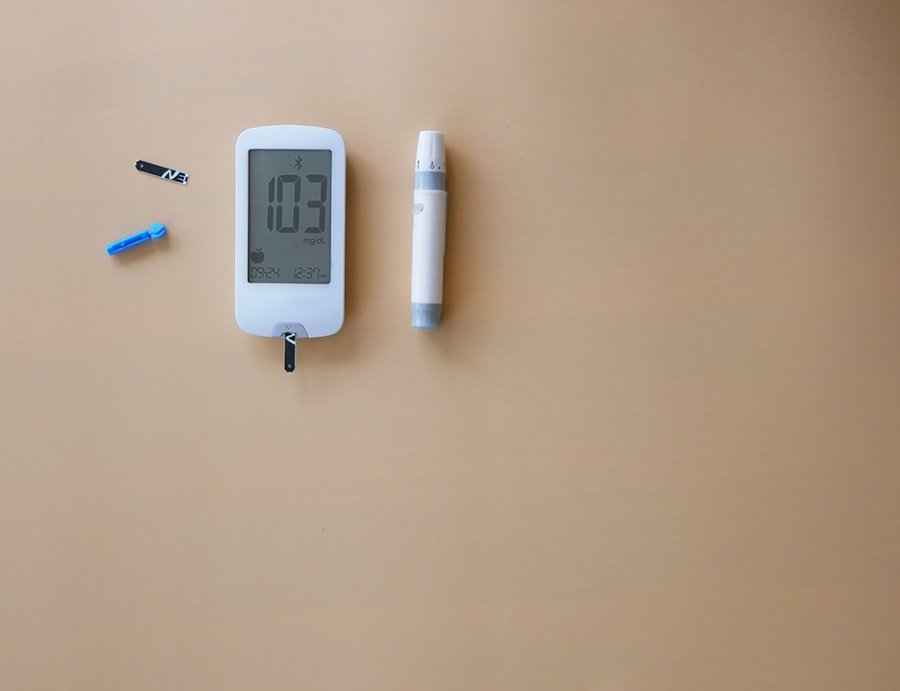
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of managing Type 1 diabetes effectively. Individuals with this condition must regularly check their blood glucose levels to ensure they remain within a target range. This is typically done using a glucometer, a device that provides a quick reading of blood sugar levels from a small drop of blood.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) have also gained popularity in recent years, offering real-time data on glucose fluctuations throughout the day and night. These devices can alert users to potential highs or lows, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent serious complications. Regular monitoring not only helps in maintaining optimal blood sugar levels but also aids in understanding how different foods, activities, and stressors affect glucose levels.
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring can vary based on individual needs and treatment plans. Some people may need to check their levels multiple times a day, especially before meals and bedtime, while others may require less frequent checks. Keeping a detailed log of blood sugar readings can provide valuable insights into patterns and trends over time, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their insulin doses and lifestyle choices.
Additionally, understanding the impact of factors such as diet, exercise, illness, and hormonal changes on blood sugar levels is essential for effective management. By staying attuned to their body’s signals and maintaining consistent monitoring practices, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
Meal Planning and Nutrition
Meal planning and nutrition play a pivotal role in managing Type 1 diabetes effectively. A well-balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels while providing essential nutrients for overall health. Individuals with this condition must pay close attention to carbohydrate intake since carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood glucose levels.
Understanding how different foods affect blood sugar is crucial; for instance, complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are digested more slowly than simple sugars found in sweets and processed foods. This slower digestion helps prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, making it an important consideration when planning meals. In addition to carbohydrate counting, portion control is another vital aspect of meal planning for those with Type 1 diabetes.
Balancing macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—can help stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day. Incorporating fiber-rich foods can also aid in digestion and promote satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Furthermore, regular meal timing is essential; eating at consistent intervals helps maintain stable blood glucose levels and prevents extreme fluctuations.
Collaborating with a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes management can provide personalized guidance on meal planning and nutrition strategies tailored to individual preferences and lifestyle needs. By prioritizing healthy eating habits, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can enhance their overall well-being while effectively managing their condition.
Exercise and Physical Activity
| Category | Metrics |
|---|---|
| Exercise Frequency | 3-5 times per week |
| Duration | 30-60 minutes per session |
| Intensity | Moderate to vigorous |
| Types of Exercise | Aerobic, strength training, flexibility exercises |
| Benefits | Improved cardiovascular health, muscle strength, flexibility, and mental well-being |
Engaging in regular physical activity is an integral component of managing Type 1 diabetes effectively. Exercise not only contributes to overall health but also plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels. Physical activity increases insulin sensitivity, meaning that the body requires less insulin to lower blood glucose levels after exercise.
This effect can last for several hours post-activity, making it essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes to monitor their blood sugar before, during, and after exercise sessions. Different types of exercise—whether aerobic activities like running or swimming or strength training—can have varying effects on blood glucose levels, necessitating careful planning and adjustment of insulin doses as needed. Incorporating exercise into daily routines can also provide psychological benefits that are particularly important for individuals managing a chronic condition like Type 1 diabetes.
Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall quality of life. However, it is crucial for individuals to find activities they enjoy to maintain motivation over the long term. Setting realistic goals and gradually increasing activity levels can help build confidence and establish a sustainable exercise routine.
Additionally, staying hydrated and having quick sources of glucose on hand during workouts can help prevent hypoglycemia during physical activity. By embracing an active lifestyle, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can improve their physical health while fostering emotional resilience.
Managing Stress and Mental Health
Managing stress and mental health is an often-overlooked aspect of living with Type 1 diabetes. The constant demands of monitoring blood sugar levels, administering insulin, and making dietary choices can lead to feelings of anxiety or overwhelm. Moreover, the fear of potential complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes can exacerbate stress levels.
It is essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes to recognize the impact that stress can have on their overall well-being and blood sugar control. Stress hormones such as cortisol can lead to increased blood sugar levels, creating a challenging cycle that requires proactive management strategies. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques into daily routines can significantly improve mental health outcomes for those living with Type 1 diabetes.
Mindfulness practices such as meditation or yoga can help individuals cultivate a sense of calm and improve emotional regulation. Additionally, engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy can serve as effective distractions from daily stressors related to diabetes management. Seeking support from mental health professionals or joining support groups specifically for individuals with diabetes can also provide valuable coping strategies and foster a sense of community.
By prioritizing mental health alongside physical health, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can enhance their overall quality of life and better navigate the challenges associated with their condition.
Medication and Insulin Management
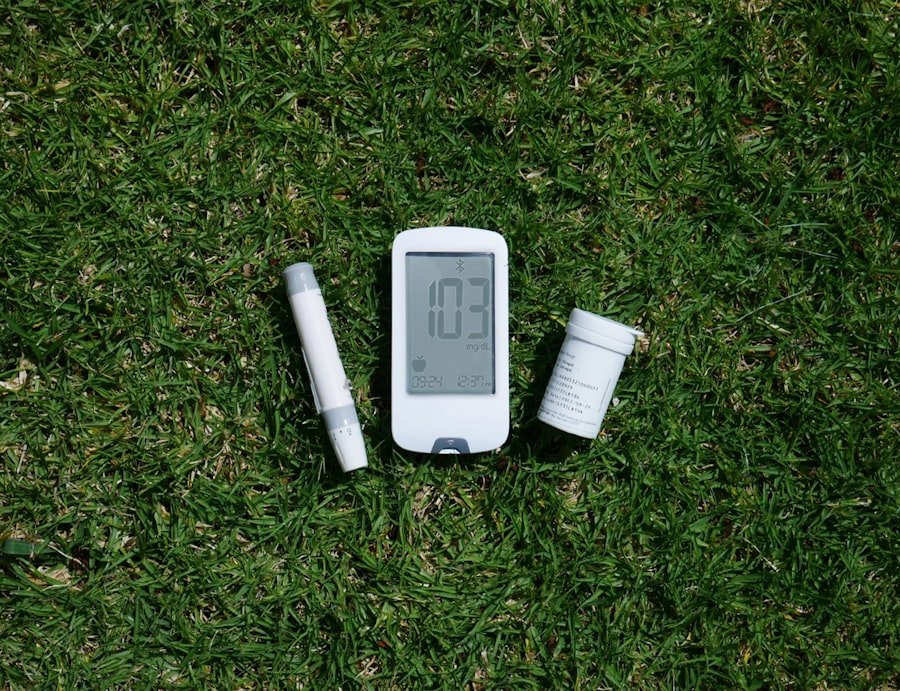

Effective medication management is crucial for individuals living with Type 1 diabetes, as insulin therapy is the primary treatment modality for this condition. Since the body cannot produce insulin on its own due to the destruction of beta cells in the pancreas, individuals must administer insulin through injections or an insulin pump. There are various types of insulin available—rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting—each serving different purposes in managing blood glucose levels throughout the day.
Understanding how these different types of insulin work is essential for effective dosing and timing around meals and physical activity. Insulin management requires careful consideration of various factors that influence blood sugar levels, including food intake, exercise routines, stress levels, and even hormonal changes during menstruation or illness. Individuals must learn how to calculate their insulin-to-carbohydrate ratios and adjust doses based on their unique needs.
Regular communication with healthcare providers is vital for optimizing insulin regimens; adjustments may be necessary based on ongoing monitoring of blood glucose patterns. Additionally, advancements in technology such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and automated insulin delivery systems are revolutionizing insulin management by providing real-time data that allows for more precise dosing decisions. By staying informed about medication options and actively participating in their treatment plans, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can achieve better glycemic control.
Regular Doctor Visits and Check-ups
Regular doctor visits and check-ups are essential components of effective Type 1 diabetes management. These appointments provide opportunities for healthcare providers to monitor an individual’s overall health status while assessing how well they are managing their diabetes. During these visits, healthcare professionals typically review blood glucose logs, discuss any challenges faced in daily management, and evaluate the effectiveness of current treatment plans.
Routine laboratory tests such as HbA1c measurements are conducted to assess long-term blood sugar control; maintaining an HbA1c level within target ranges is crucial for reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. In addition to monitoring glycemic control, regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to screen for potential complications related to Type 1 diabetes. These may include eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy, foot examinations to prevent ulcers or infections, and kidney function tests to identify early signs of diabetic nephropathy.
Establishing a strong relationship with healthcare providers fosters open communication about any concerns or questions that may arise between visits. Furthermore, staying up-to-date on vaccinations and preventive care measures is vital for individuals with Type 1 diabetes since they may be at higher risk for certain infections or illnesses. By prioritizing regular medical appointments, individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining their health while effectively managing their diabetes.
Building a Support System
Building a robust support system is invaluable for individuals living with Type 1 diabetes as they navigate the complexities of managing their condition. A strong network of family members, friends, healthcare professionals, and support groups can provide emotional encouragement while offering practical assistance when needed. Sharing experiences with others who understand the challenges associated with Type 1 diabetes fosters a sense of belonging and reduces feelings of isolation that may arise from living with a chronic illness.
Family members play a crucial role in this support system by learning about the condition themselves; their understanding can help create an environment conducive to healthy habits. In addition to personal relationships, connecting with local or online support groups dedicated to Type 1 diabetes can offer valuable resources and insights from others facing similar challenges. These groups often provide educational materials, host events or workshops focused on diabetes management strategies, and create opportunities for social interaction among members.
Engaging with peers who share similar experiences allows individuals to exchange tips on coping mechanisms or share success stories that inspire motivation in others facing similar struggles. By actively cultivating a supportive community around them, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can enhance their resilience while fostering a positive outlook on living with this chronic condition.
FAQs
What is T1DM?
T1DM stands for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, which is a chronic condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin. This results in high blood sugar levels and requires regular insulin injections for management.
What are the symptoms of T1DM?
Common symptoms of T1DM include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and irritability. If left untreated, T1DM can lead to serious complications.
How is T1DM diagnosed?
T1DM is diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels and levels of specific antibodies that attack the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. A healthcare professional will also consider the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
What are the treatment options for T1DM?
The main treatment for T1DM is insulin therapy, which involves regular injections or the use of an insulin pump. Patients also need to monitor their blood sugar levels, follow a healthy diet, and engage in regular physical activity.
What are the potential complications of T1DM?
Untreated or poorly managed T1DM can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. It is important for individuals with T1DM to work closely with healthcare professionals to prevent and manage these complications.
Can T1DM be prevented?
Currently, there is no known way to prevent T1DM. It is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and it is not related to lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise.
